When designing a solar energy or power distribution system, you will face a crucial decision, that is, to choose an AC combiner box or a DC combiner box? Although both types of combiner boxes have similar purposes – integrating multiple electrical inputs into one output, their designs, components and applications are quite different.
Fundamental Differences in Current Handling
Characteristics | DC Combiner Boxes | AC Combiner Boxes |
| Position | Positioned on the input side of solar inverters, handling direct current (DC) from solar panels. | Works on the output side of inverters, combining multiple alternating current (AC) outputs from inverters into a single feed that connects to your electrical panel or grid connection. |
| Operation | Operates before inversion: Handles raw DC power directly from solar panels | Operates after inversion: Handles AC power converted by inverters |
| Voltage Handling | Higher voltage handling: Typically manages voltages between 600V-1500V DC | Standard voltage levels: Typically handles 120V, 208V, 240V, or 480V AC |
| Protection | String protection: Includes fuses or circuit breakers for each string | Inverter protection: Includes circuit breakers for each inverter output |
| Surge Protection | Surge protection: Protects against lightning strikes and voltage spikes | Grid compliance: Ensures synchronization with utility power standards |
| Monitoring | Monitoring capability: Advanced models include string-level monitoring | Disconnect functionality: Provides a central point for system shutdown |
| Applicability | DC combiners are essential for large-scale installations where multiple panel strings need consolidation before reaching the inverter. | AC combiners are particularly valuable in systems with multiple microinverters or when combining outputs from several string inverters. |
What Are the Key Technical Distinctions Between AC and DC Combiner Boxes?
Voltage Characteristics
- DC junction boxes handle high-voltage DC electricity, which presents unique safety challenges. DC arcs can sustain themselves longer than AC arcs and require specialized safety disconnects.
- AC junction boxes work with standard AC voltages that follow typical building electrical standards, making them somewhat easier to work with from a safety perspective.
Safety Considerations
- DC distribution box require arc-fault detection and rapid shutdown capabilities to mitigate fire risks associated with high-voltage DC. They must comply with NEC requirements for rapid shutdown.
- AC distribution box primarily deal with overcurrent protection and proper grounding. They must meet UL and NEC standards for panelboards.
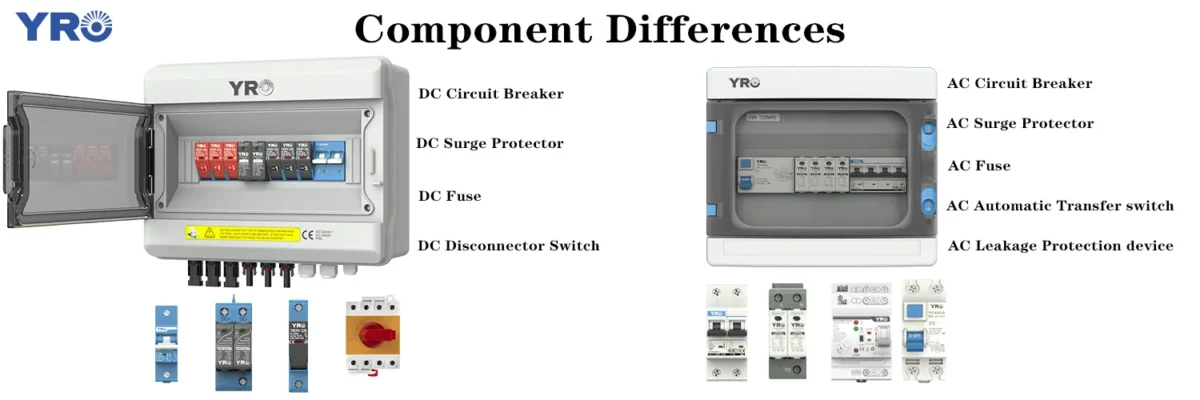
Component Differences
- DC box use DC-rated fuses, breakers, and disconnects specifically designed for DC applications. Standard AC components cannot be substituted due to arc-extinguishing challenges.
- AC box use standard AC electrical components that are readily available and less expensive than their DC counterparts.
 Application Scenarios
Application Scenarios
When to Use a DC Junction Box?
- Central inverter systems with multiple solar panel strings
- Large-scale commercial or utility solar installations
- Systems where long DC cable runs are unavoidable
- Installations requiring string-level monitoring
When to Use an AC Junction Box?
- Microinverter-based solar installations
- Systems with multiple string inverters
- Commercial installations with numerous small inverters
- When consolidating AC outputs before the main distribution panel
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
DC distribution boxes require specialized installation knowledge due to the hazards of high-voltage DC. Technicians need specific training and tools for safe installation and maintenance. Regular inspection of DC connections is critical as loose connections can lead to dangerous arcing.
AC distribution installation follows standard electrical practices familiar to most electricians. Maintenance typically involves routine checks of connections and ensuring breakers operate correctly. Since AC distributions handle lower voltages after inversion, safety risks during maintenance are reduced.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between AC and DC distribution boxes is essential for designing solar installations that are safe, efficient, and compliant with regulations. This choice is not arbitrary—it depends on your system architecture and component selection.
By choosing a trusted manufacturer like YRO, you ensure that your box (whether AC or DC) meets high-quality standards. With over 10 years of manufacturing expertise, YRO controls the entire process from design to assembly, delivering customized combiner solutions for today’s solar and electrical systems.

 Application Scenarios
Application Scenarios







