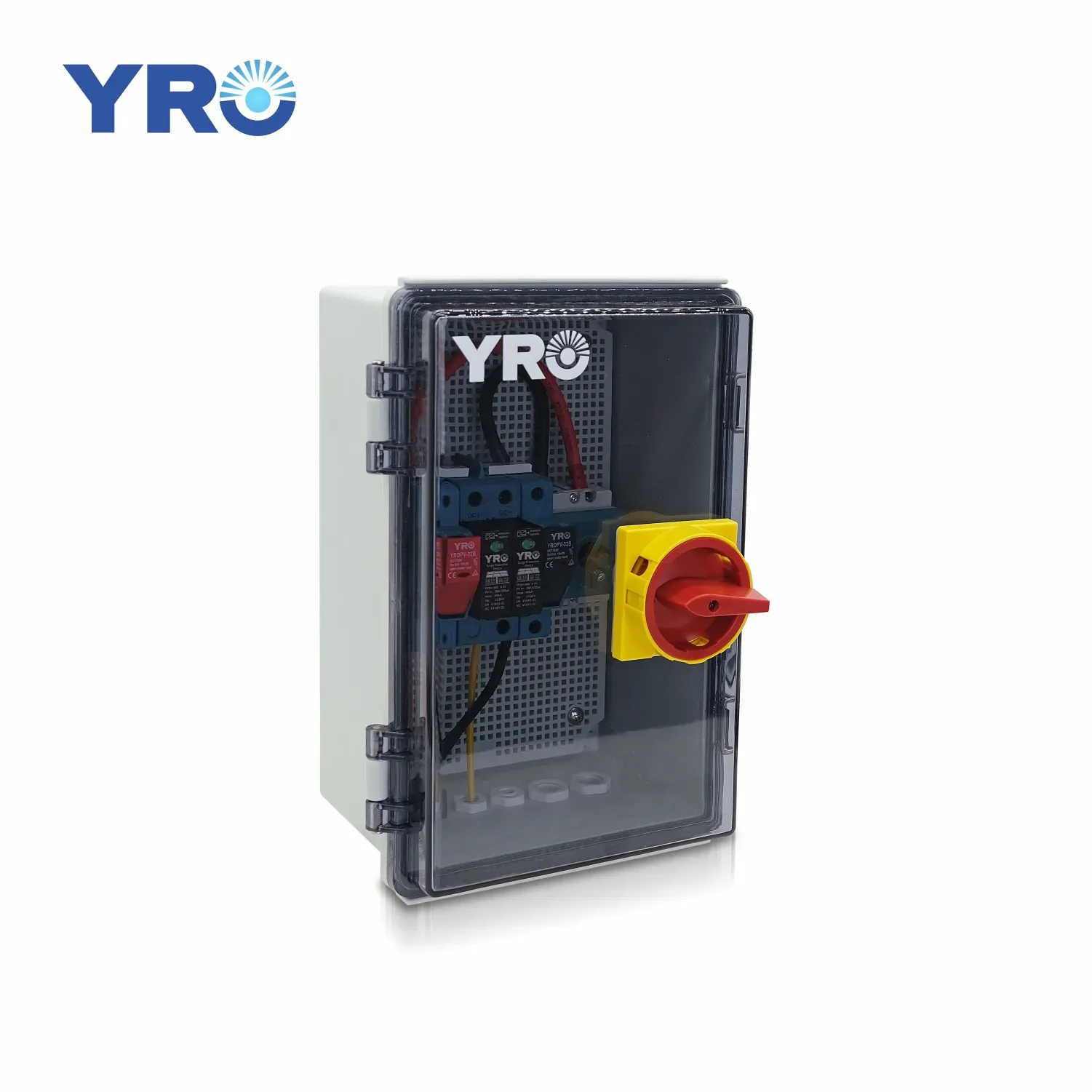
In modern electrical systems, circuit breakers, as crucial safety protection devices, determine the reliability of the power system. However, many engineers and users often face a dilemma when choosing a circuit breaker: is a common circuit breaker sufficient, or do they need to use a molded case circuit breaker? If the wrong circuit breaker is chosen, it may lead to inadequate protection, causing short circuits, equipment damage, and even serious electrical fires, endangering personal and property safety. In addition, an unsuitable circuit breaker may increase maintenance costs, reduce system stability, and expose enterprises to higher operational risks. Therefore, having an in depth understanding of the differences between molded case circuit breakers, and common circuit breakers is essential for ensuring the safety of electrical systems.
Common circuit breakers are primarily used for protecting against overloads and short circuits, and they are commonly found in household electrical systems. In contrast, molded case circuit breakers (MCCBs) typically serve as low voltage main switches, such as those used in switchgear.
When compared side by side, MCCBs offer a more comprehensive set of functions. Not only do they provide the same protection as common circuit breakers, but they also feature the ability to issue an overload alarm without immediately tripping the circuit. Additionally, they support reverse power input and can be equipped with various accessories to meet diverse application needs.
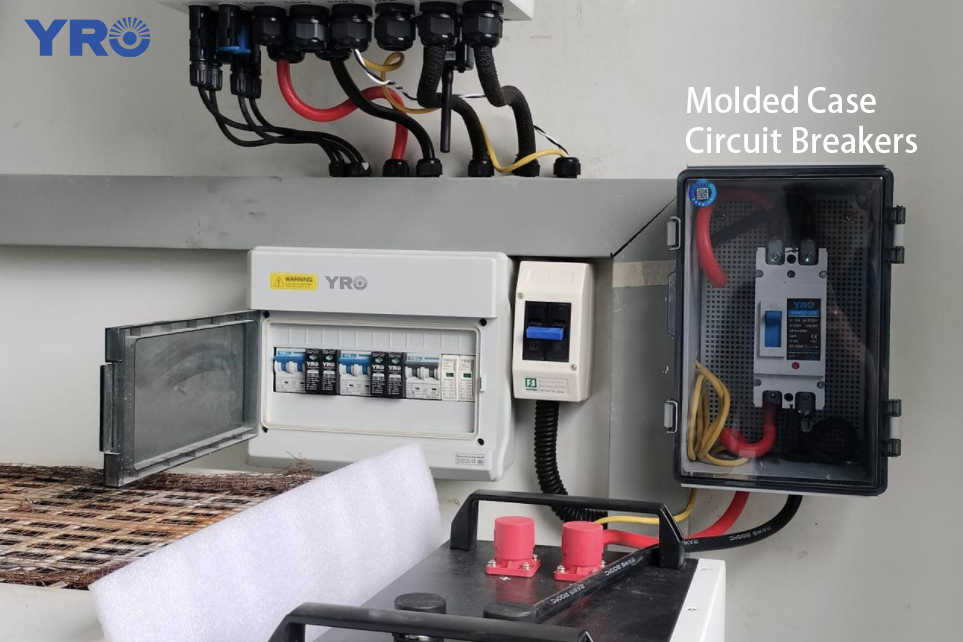 A brief look at these two types of circuit breakers, gives us a rough idea of the advantages of molded case circuit breakers in terms of safety, reliability, and where they can be used. Now, you may want to know the difference between them in terms of technical details. When choosing, how do we determine the parameters? Below we will analyze several aspects in depth to help you make a more informed choice.
A brief look at these two types of circuit breakers, gives us a rough idea of the advantages of molded case circuit breakers in terms of safety, reliability, and where they can be used. Now, you may want to know the difference between them in terms of technical details. When choosing, how do we determine the parameters? Below we will analyze several aspects in depth to help you make a more informed choice.
What Are the Differences Between Molded Case Circuit Breakers and Regular Circuit Breakers?
Current magnitude
Moulded case circuit breakers are rated for currents of 1600A or more, compared to ordinary miniature circuit breakers, which typically have a maximum current of no more than 125A. In contrast, ordinary miniature circuit breakers usually have a maximum current of no more than 125 A. Because of this huge difference in current handling capacity, molded case circuit breakers require a much larger effective wiring area. MCCB are usually used for wires with a cross sectional area of more than 35 square millimeters. Miniature circuit breakers, on the other hand, are suitable for wires with a cross sectional area of less than 10 square millimeters. Therefore, for indoor installations where space is at a premium, molded case CB are usually preferred.
Protection mechanism
MCCB use independent overcurrent and short circuit protection devices, and the action value of the overcurrent protection is adjustable, which is suitable for different load requirements. In contrast, common circuit breakers share a set of overcurrent and short circuit protection devices, and the current is not adjustable, making them suitable for the protection of circuits with fixed loads.
Structural design
Molded case circuit breakers have a larger phase to phase distance and are equipped with arc extinguishers, having stronger arc extinguishing capabilities. Therefore, they can withstand higher short circuit currents and reduce the risk of phase to phase short circuits. Common circuit breakers are compact in size and pay more attention to sensitivity, making them suitable for the protection of terminal loads that require a quick response.
Scope of application
Molded case circuit breakers are widely used in industrial, commercial, and large scale power systems and can meet the needs of different voltage levels. Common circuit breakers are more often used in households or small scale electrical systems. Their response to short circuits and overloads is more basic, making them suitable for simple circuit protection scenarios.
How to Choose the Right Molded Case Circuit Breaker?
Determine the rated voltage and current
Electrical equipment in different locations have very different voltage and current requirements. For example, lighting fixtures in an apartment building typically use 10 amps of capacity, while machines on the factory floor often require several hundred amps. The first step in selecting industrial grade circuit protection equipment, is to accurately determine the voltage level of the power supply system, and calculate the maximum load current. If the voltage is incorrect, it’s like putting the wrong fuel in an engine, which can seriously damage equipment. And if the current carrying capacity is insufficient, it’s like a bridge that can’t handle the weight of the traffic on it, which can easily cause the circuit to trip. Only by choosing the right parameters, can we both ensure the continuous operation of the machine, and cut off the dangerous current in time when there is a sudden short circuit or overload, so as to avoid causing a bigger accident.
Select an appropriate breaking capacity
The rated breaking capacity of molded case circuit breakers is usually high. Users need to select an appropriate breaking capacity according to the actual application scenario, to ensure that the circuit can be quickly cut off in case of a short circuit fault, and prevent the accident from expanding.
Pay attention to the tripping characteristics
MCCB usually use thermal magnetic tripping or electronic tripping. The former is suitable for the protection of ordinary circuits, and the latter is suitable for more accurate current monitoring and control. When making a choice, it is necessary to combine the load characteristics, to ensure that the circuit breaker can respond to fault situations in a timely manner.
Ensure compliance with international standards
Molded case circuit breakers should comply with international or national standards, such as IEC and UL to ensure the safety and reliability of the products. When purchasing, you can check whether the products have passed the corresponding certifications to ensure that they meet industry specifications.
Conclusion
Whether it is a molded case circuit breaker or a common circuit breaker, both are directly related to the safe and stable operation of the electrical system. By having an in depth understanding of product characteristics and system requirements, not only can the risk of equipment failure be effectively reduced, but also higher economic benefits and safety guarantees can be achieved in the long term operation. It is hoped that this article provides you with valuable references to help you better optimize the power system, improve operation efficiency, and reduce the risk of failures.