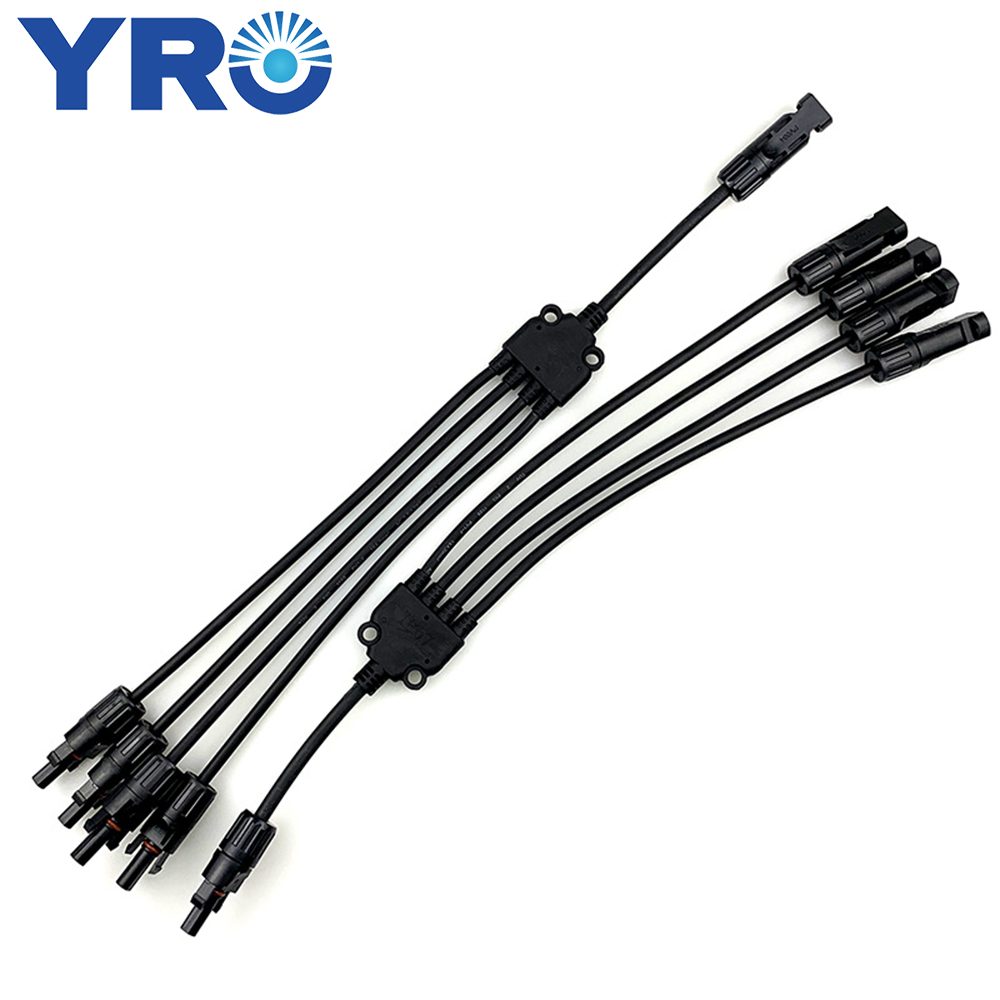
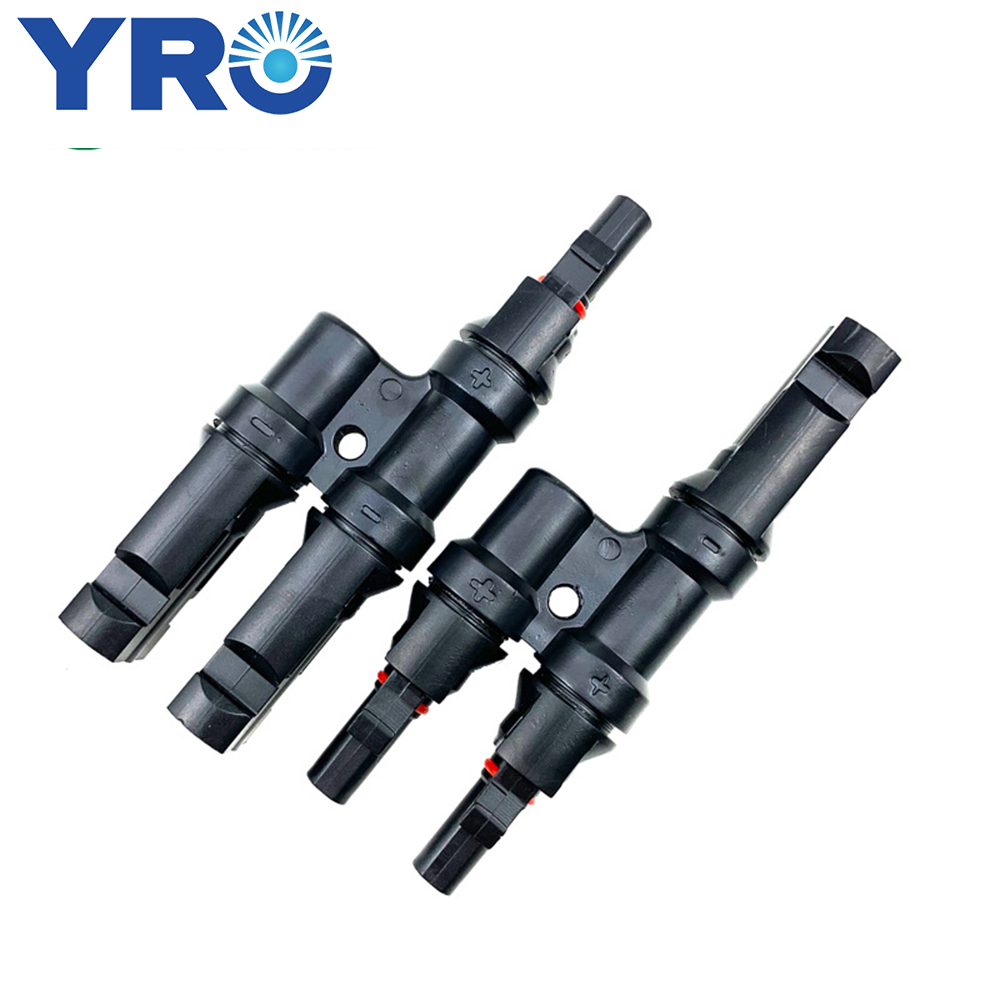
Một bài kiểm tra lão hóa UV, còn được gọi là bài kiểm tra thời tiết UV hoặc bài kiểm tra phơi sáng UV, là một bài kiểm tra trong phòng thí nghiệm được thực hiện để đánh giá tác động của bức xạ cực tím (UV) lên vật liệu, sản phẩm hoặc mẫu trong một khoảng thời gian xác định. Mục đích của bài kiểm tra này là mô phỏng sự phơi sáng lâu dài đối với bức xạ UV mà vật liệu và sản phẩm có thể trải qua khi tiếp xúc với ánh sáng mặt trời và các nguồn bức xạ UV khác trong môi trường ngoài trời.
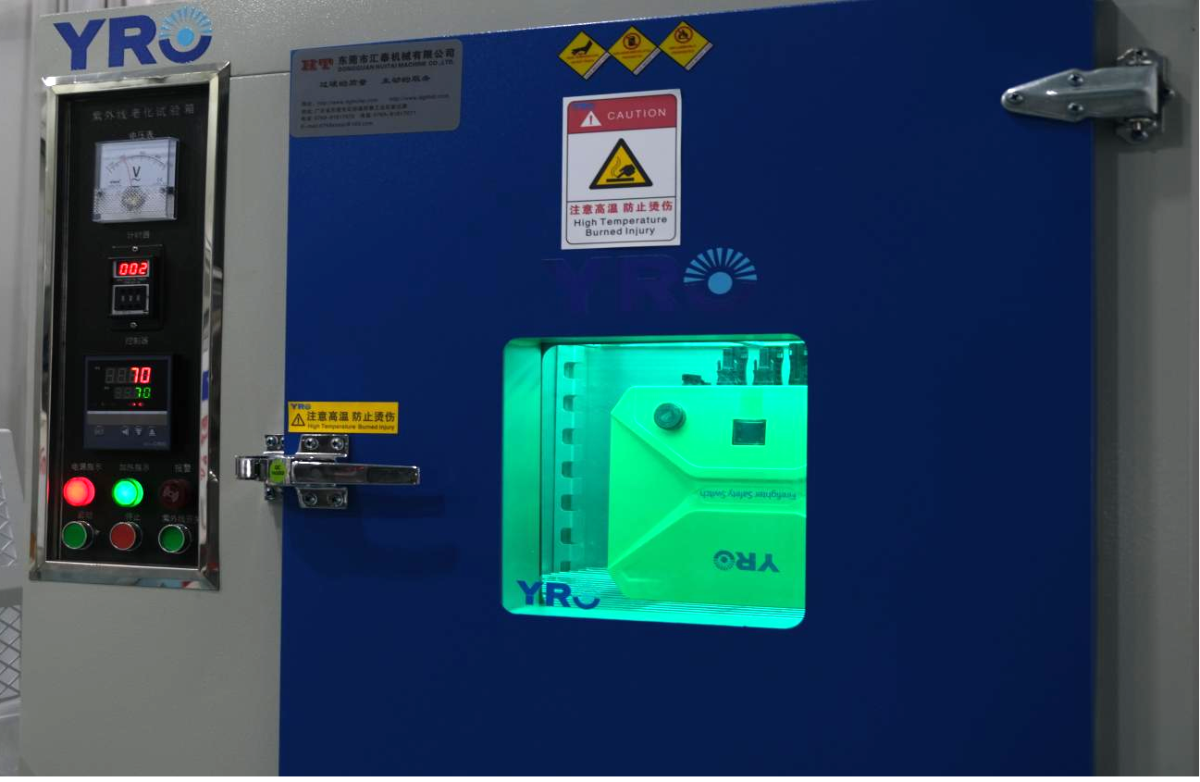

Bức xạ UV từ mặt trời có thể gây ra nhiều hình thức suy thoái và hư hỏng ở vật liệu và sản phẩm, bao gồm:
- Phai Màu: Bức xạ UV có thể dẫn đến sự phai màu ở các vật liệu như vải, sơn, nhựa và lớp phủ.
- Suy Giảm Vật Liệu: Sự tiếp xúc với bức xạ UV có thể làm phá vỡ cấu trúc phân tử của vật liệu, dẫn đến tình trạng nứt, giòn và giảm sức mạnh cơ học.
- Bề Mặt Phấn: Một số vật liệu có thể phát triển bề mặt bột hoặc phấn khi tiếp xúc với bức xạ UV.
- Vàng Hoá: Nhựa và các vật liệu khác có thể bị vàng hoặc mất màu khi tiếp xúc với bức xạ UV.
- Mất Độ Trong Suốt: Các vật liệu trong suốt như kính và nhựa có thể trở nên đục hoặc mất đi độ trong suốt theo thời gian.
Các bài kiểm tra lão hóa UV liên quan đến việc đưa các mẫu thử nghiệm vào các mức bức xạ UV kiểm soát, thường sử dụng đèn UV đặc biệt hoặc buồng phát ra ánh sáng UV theo cách có kiểm soát. Các mẫu được tiếp xúc với bức xạ UV trong một số giờ hoặc ngày xác định, tùy thuộc vào yêu cầu của bài kiểm tra. Các điều kiện, bao gồm cường độ UV và nhiệt độ, được kiểm soát chặt chẽ để mô phỏng các điều kiện thực tế một cách chính xác nhất có thể.
Sau khoảng thời gian tiếp xúc, các mẫu sẽ được đánh giá về bất kỳ thay đổi hoặc suy thoái nào xảy ra do sự tiếp xúc với UV. Việc đánh giá này có thể bao gồm việc đo lường sự thay đổi màu sắc, sự thay đổi trong các thuộc tính vật liệu và kiểm tra trực quan các hư hỏng bề mặt.
Các bài kiểm tra lão hóa UV thường được sử dụng trong các ngành công nghiệp như ô tô, hàng không, xây dựng, dệt may và nhựa để đánh giá độ bền và hiệu suất của vật liệu và sản phẩm khi tiếp xúc với bức xạ UV. Kết quả của những bài kiểm tra này có thể giúp các nhà sản xuất đưa ra quyết định có thông tin về việc chọn lựa vật liệu, thiết kế sản phẩm và tuổi thọ dự kiến của sản phẩm trong các môi trường ngoài trời hoặc bị phơi nhiễm UV.
Lợi ích của việc Kiểm Tra Lão Hóa UV
- Đánh Giá Độ Bền Vật Liệu: Các bài kiểm tra lão hóa UV giúp đánh giá cách mà vật liệu và sản phẩm sẽ hoạt động khi tiếp xúc với bức xạ UV kéo dài. Điều này đặc biệt quan trọng cho các ứng dụng ngoài trời, vì nó cho phép các nhà sản xuất chọn các vật liệu có thể chịu đựng các điều kiện môi trường và duy trì tính toàn vẹn theo thời gian.
- Kiểm Soát Chất Lượng: Các nhà sản xuất có thể sử dụng thử nghiệm lão hóa UV như một công cụ kiểm soát chất lượng để đảm bảo rằng sản phẩm của họ đạt tiêu chuẩn về độ bền và hiệu suất. Bằng cách đưa các mẫu vào lão hóa UV tăng tốc, họ có thể xác định các vấn đề tiềm năng và thực hiện các điều chỉnh về thiết kế hoặc vật liệu trước khi sản phẩm ra thị trường.
- Phát Triển Sản Phẩm: Thử nghiệm lão hóa UV có giá trị trong giai đoạn phát triển sản phẩm. Nó giúp các kỹ sư và nhà thiết kế chọn lựa vật liệu phù hợp nhất và thực hiện các cải tiến về thiết kế để nâng cao khả năng kháng lại sự suy thoái do UV gây ra. Điều này có thể dẫn đến việc tạo ra các sản phẩm bền lâu hơn và đáng tin cậy hơn.
- Tiết Kiệm Chi Phí: Việc xác định sớm các điểm yếu về vật liệu hoặc thiết kế trong quá trình phát triển có thể dẫn đến tiết kiệm chi phí bằng cách ngăn ngừa các cuộc gọi thu hồi tốn kém, các yêu cầu bảo hành và hư hỏng sản phẩm tại hiện trường. Nó cho phép các công ty đầu tư vào các vật liệu và thiết kế mang lại hiệu suất tốt hơn trong dài hạn.
- Tuân Thủ Quy Định: Một số ngành công nghiệp, như ô tô và hàng không, có các quy định và tiêu chuẩn nghiêm ngặt về hiệu suất và độ bền của vật liệu và linh kiện bị phơi nhiễm với bức xạ UV. Kiểm tra lão hóa UV có thể giúp đảm bảo tuân thủ các quy định này.
- Bảo Trì Dự Đoán: Trong các lĩnh vực như cơ sở hạ tầng và xây dựng, thử nghiệm lão hóa UV có thể được sử dụng để dự đoán nhu cầu bảo trì cho các kết cấu và vật liệu ngoài trời, giúp lên kế hoạch cho các sửa chữa hoặc thay thế cần thiết trước khi sự suy thoái đáng kể xảy ra.
- Sự Tin Tưởng Của Người Tiêu Dùng: Chứng minh rằng sản phẩm đã trải qua các thử nghiệm lão hóa UV nghiêm ngặt và có thể chịu đựng được sự phơi sáng UV có thể gia tăng sự tin tưởng của người tiêu dùng. Nó cũng có thể phục vụ như một lợi thế tiếp thị, đặc biệt là cho các sản phẩm ngoài trời và bị phơi nhiễm UV.
- Nghiên Cứu và Phát Triển: Các nhà nghiên cứu có thể sử dụng thử nghiệm lão hóa UV để nghiên cứu các cơ chế suy thoái của vật liệu dưới bức xạ UV, dẫn đến hiểu biết sâu sắc hơn về hành vi của vật liệu và các đổi mới tiềm năng trong khoa học vật liệu.
- Xác thực bảo hành dài hạn: Các nhà sản xuất có thể sử dụng thử nghiệm tuổi thọ UV để xác thực bảo hành dài hạn trên các sản phẩm, vì họ có thể chứng minh rằng sản phẩm của họ đã được thử nghiệm trong các điều kiện mô phỏng sự tiếp xúc với UV trong thế giới thực.
- Đánh giá tác động môi trường: Thử nghiệm tuổi thọ UV có thể giúp đánh giá tác động môi trường của các vật liệu và sản phẩm, vì nó mô phỏng tác động của việc tiếp xúc kéo dài với ánh sáng mặt trời và bức xạ UV, điều này có thể góp phần vào sự phân hủy của các vật liệu và phát thải các chất độc hại.

Tóm lại, thử nghiệm tuổi thọ UV là một công cụ quý giá để đánh giá độ bền, hiệu suất và độ tin cậy của các vật liệu và sản phẩm tiếp xúc với bức xạ UV. Nó góp phần nâng cao chất lượng sản phẩm, tuổi thọ và sự hài lòng tổng thể của khách hàng trong khi giúp các nhà sản xuất đáp ứng các tiêu chuẩn và quy định của ngành.









