An Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS) is an electrical device that is used to automatically switch the power source of an electrical load between two sources, typically between the utility power grid and a backup power source such as a generator or an uninterruptible power supply (UPS). ATS is commonly used in situations where a continuous and uninterrupted power supply is critical, such as in data centers, hospitals, emergency response facilities, and critical industrial processes.
Here’s how an Automatic Transfer Switch typically works:
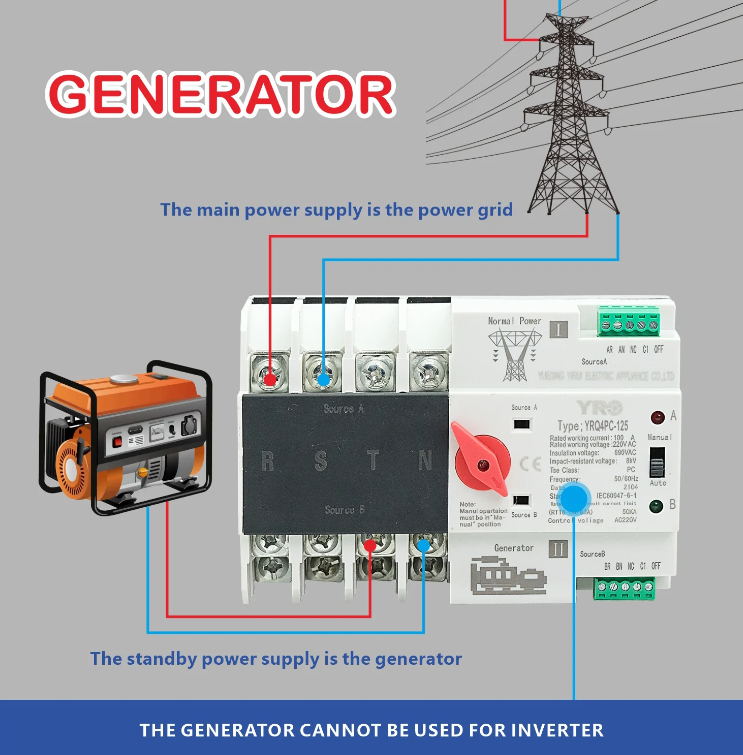

——Normal Power Source: The ATS is normally connected to the primary power source, which is usually the utility power grid. When the utility power supply is stable and available, the ATS continuously monitors its quality.
——Backup Power Source: In the event of a power outage or a significant disturbance in the utility power supply, the ATS is designed to automatically detect the issue. It will then initiate a transfer to the backup power source, which could be a generator or a UPS system.
——Transfer Process: During the transfer process, the ATS switches the load from the normal power source to the backup power source. This ensures that the connected electrical equipment continues to receive power without interruption.
——Reversion: Once the utility power is restored and stabilized, the ATS will again monitor it. When the utility power supply becomes reliable, the ATS will automatically switch the load back to the normal power source and disconnect it from the backup source.
Automatic Transfer Switch systems are crucial for maintaining uninterrupted power in critical applications, as they reduce the downtime associated with power interruptions. They also help protect sensitive equipment and prevent data loss in situations where a stable power supply is essential.
Automatic Transfer Switch devices come in various sizes and configurations to accommodate different power loads and requirements. They can range from small, residential ATS units that are used with standby generators to large, industrial-grade ATS systems capable of handling substantial power loads.
Advantages of Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS):
Reliability: Automatic Transfer Switch systems ensure uninterrupted power supply by automatically switching to an alternate power source, such as a generator, in the event of a power outage. This helps prevent downtime and ensures continuous operation for critical systems.
Safety: Automatic Transfer Switch systems are designed to operate safely and reliably, reducing the risk of manual errors during power transfers. They provide isolation between power sources, preventing backfeeding and electrical hazards.
Convenience: Automatic Transfer Switch systems automate the power transfer process, eliminating the need for manual intervention during power outages. This is especially valuable for businesses and facilities that require constant power, such as data centers and healthcare facilities.
Fast Switching: Automatic Transfer Switch units can switch power sources quickly, often in a matter of milliseconds. This rapid transfer minimizes disruptions and ensures that sensitive equipment remains powered without interruption.
Monitoring and Control: Many modern ATS systems offer monitoring and control features, allowing users to remotely monitor the status of the ATS and initiate transfers as needed. This enhances operational control and allows for proactive maintenance.
Load Management: Some ATS systems offer load shedding capabilities, allowing users to prioritize power distribution to essential equipment during generator operation. This helps optimize generator usage and reduces fuel consumption.
Scalability: ATS systems can be installed in various configurations to accommodate different power needs and system sizes. They can be customized to meet specific requirements.
In summary, ATS systems offer significant advantages in terms of reliability, safety, and convenience when it comes to maintaining uninterrupted power supply. However, they come with initial costs, maintenance requirements, and potential complexities that should be carefully considered when planning their installation. Proper maintenance and periodic testing are essential to ensure the continued reliability of an ATS system.
What Is the Difference Between ATS and STS?
The difference between ATS and STS (Static Transfer Switch) lies in their switching speed, working principles, applications, and other features.
| Feature | ATS (Automatic Transfer Switch) | STS (Static Transfer Switch) |
| Switching Speed | Slower (tens of milliseconds to seconds) | Faster (usually within milliseconds) |
| Working Principle | Electromagnetic relays or mechanical contactors | Solid state components (thyristors, IGBTs) |
| Applications | Suitable for general loads, such as general industrial equipment, commercial buildings, as well as certain medical and telecom systems. | Suitable for critical loads where power interruption is unacceptable, such as data centers, financial systems, precision medical devices, and industrial automation. |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Maintenance | Requires periodic inspection of mechanical parts | Less maintenance, but requires check on heat dissipation and electrical protection |
What Is the Life Expectancy of an Automatic Transfer Switch?
Generally, under normal use and maintenance conditions, the life expectancy of an Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS) can reach around 10 years. However, this is not an absolute figure, as it is influenced by multiple factors:
1、Material Quality: The internal structure and materials used in an ATS have a critical impact on its lifespan. High-quality materials and precision engineering can significantly improve the switch’s durability and stability.
2、Usage Frequency: Frequent power switching accelerates the wear and tear on the ATS’s mechanical components, thereby affecting its longevity. Therefore, usage frequency is an important factor when assessing switch lifespan.
3、Operating Environment: Harsh conditions such as high temperature, humidity, and dust can negatively impact the device’s lifespan. Conversely, a clean, well-controlled environment can help extend its operational life.
4、Load Type: If the load is highly variable or exceeds the switch’s rated capacity, it may accelerate component aging and reduce the overall lifespan.
