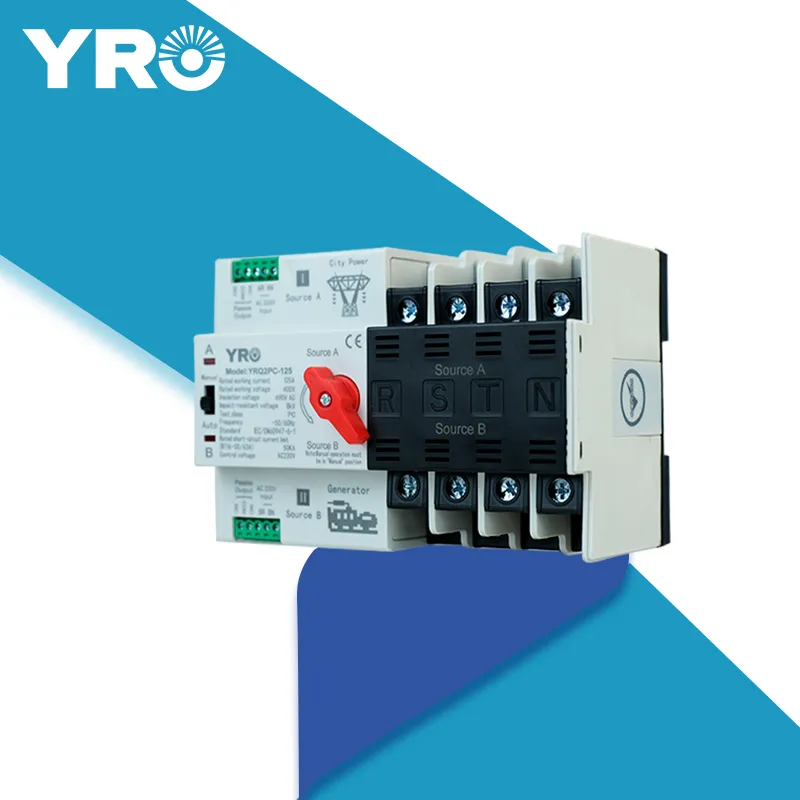
MCCB (Cầu dao tự động vỏ khuôn)
A MCCB (Cầu dao tự động vỏ khuôn) là một loại thiết bị bảo vệ điện nhằm bảo vệ các mạch khỏi các lỗi như quá tải, ngắn mạch và lỗi đất. Thuật ngữ “vỏ khuôn” đề cập đến vỏ cách điện được làm từ vật liệu nhựa chịu lực cao, chống va đập, bao bọc thiết bị, cung cấp cả cách điện và bảo vệ cho các thành phần bên trong. MCCB là những thiết bị đa năng thường được sử dụng trong các hệ thống điện công nghiệp, thương mại và dân cư để đảm bảo bảo vệ mạch và độ tin cậy tổng thể của hệ thống.
I. MCCB là gì?
MCCB là những cầu dao được thiết kế đặc biệt có cơ chế bảo vệ quá dòng nhiệt và từ điện tử. Những thiết bị này có khả năng cung cấp bảo vệ mạch đáng tin cậy trong nhiều tình huống ứng dụng bằng cách phát hiện và phản ứng với các điều kiện điện bất thường. Khi xảy ra tình trạng lỗi như quá tải hoặc ngắn mạch, MCCB tự động ngắt mạch, qua đó ngăn chặn thiệt hại tiềm ẩn cho thiết bị điện, dây điện hoặc thậm chí là ngăn chặn hỏa hoạn.
 II. Một cầu dao tự động vỏ khuôn tiêu chuẩn chứa những gì?
II. Một cầu dao tự động vỏ khuôn tiêu chuẩn chứa những gì?
Để hiểu rõ chức năng và tầm quan trọng của một MCCB, cần thiết phải hiểu các thành phần chính của nó và cách chúng hoạt động cùng nhau để cung cấp bảo vệ. Một MCCB tiêu chuẩn bao gồm một số bộ phận thiết yếu, mỗi bộ phận phục vụ một mục đích cụ thể:
- Vỏ: Vỏ được làm từ các vật liệu cách điện chịu nhiệt và chống va đập như polypropylene (PP) hoặc polyvinyl chloride (PVC). Vỏ này bảo vệ các thành phần bên trong khỏi các yếu tố môi trường và cung cấp cách điện để ngăn ngừa nguy cơ điện.
- Chân tiếp xúc: Các chân tiếp xúc có trách nhiệm kết nối và ngắt kết nối mạch. Thông thường có hai loại chân tiếp xúc trong một MCCB - chân tiếp xúc cố định và chân tiếp xúc di động. Sự tương tác giữa các chân tiếp xúc này cho phép cầu dao mở hoặc đóng mạch.
- Cơ chế ngắt: Cơ chế ngắt bao gồm một đơn vị ngắt nhiệt và một đơn vị ngắt từ.
- Đơn vị ngắt nhiệt: Thành phần này phát hiện các dòng quá tải bằng cách sử dụng một dải kim loại hai thành phần bóp cong khi được đun nóng. Hành động uốn cong này khiến cầu dao ngắt, hiệu quả là ngắt mạch để ngăn ngừa quá nhiệt và thiệt hại thiết bị. Cơ chế này có hành động trì hoãn để phân biệt giữa các đợt tăng đột biến tạm thời và quá tải kéo dài.
- Đơn vị ngắt từ: Đơn vị ngắt từ phát hiện các dòng ngắn mạch thông qua một cuộn điện từ. Khi xảy ra ngắn mạch, cuộn tạo ra một trường điện từ mạnh mẽ ngay lập tức kích hoạt cầu dao mở, nhanh chóng bảo vệ mạch và các thiết bị kết nối.
- Cơ chế vận hành: Cơ chế này cho phép vận hành cầu dao cả bằng tay và tự động. Nó tạo điều kiện cho việc mở và đóng cầu dao và đảm bảo rằng thiết bị có thể được vận hành an toàn và hiệu quả.
- Hệ thống dập hồ quang: Hệ thống dập tắt hồ quang được thiết kế để dập tắt một cách an toàn hồ quang hình thành khi cầu chì ngắt dòng điện. Hệ thống này rất quan trọng để bảo vệ các tiếp điểm khỏi bị hư hỏng và đảm bảo tuổi thọ cho cầu chì.
- Đèn báo trạng thái: Đèn báo trạng thái cung cấp phản hồi hình ảnh về trạng thái hiện tại của cầu chì, chẳng hạn như liệu nó có đang “mở”, “đóng” hoặc đã gặp sự cố hay không. Tính năng này thường được thể hiện bằng chỉ báo cơ học hoặc đèn LED, giúp người dùng dễ dàng theo dõi và quản lý hệ thống.
- Cổng kết nối: Các cổng kết nối được sử dụng để kết nối các dây hoặc cáp vào và ra với MCCB, cho phép nó được tích hợp vào hệ thống điện.
- Tiếp điểm phụ (Tùy chọn): Các tiếp điểm phụ là các thành phần tùy chọn cho phép giám sát và điều khiển từ xa MCCB. Chúng có thể được kết nối với các hệ thống hoặc thiết bị khác để cung cấp thêm chức năng, chẳng hạn như điều khiển liên kết và cập nhật trạng thái theo thời gian thực.
Thông qua sự vận hành phối hợp của những thành phần này, cầu chì vỏ nhựa bảo vệ các hệ thống điện một cách hiệu quả và đáng tin cậy khỏi quá tải, ngắn mạch và các lỗi khác. Điều này đảm bảo an toàn cho cả thiết bị điện và nhân viên, khiến MCCB trở thành một thành phần quan trọng trong các hệ thống bảo vệ điện hiện đại.