Com o desenvolvimento da indústria global de energia solar, os regulamentos relevantes em vários países também estão a ser gradualmente melhorados. Para os fabricantes, instaladores e utilizadores de sistemas, estar informado destas alterações em tempo útil ajuda a garantir a segurança e a conformidade do sistema.
No Brasil, um importante mercado de energia solar, há uma questão notória: Existe a obrigatoriedade de instalação de dispositivos de desligamento rápido de energia solar no local?
Situação atual do desenvolvimento solar no Brasil
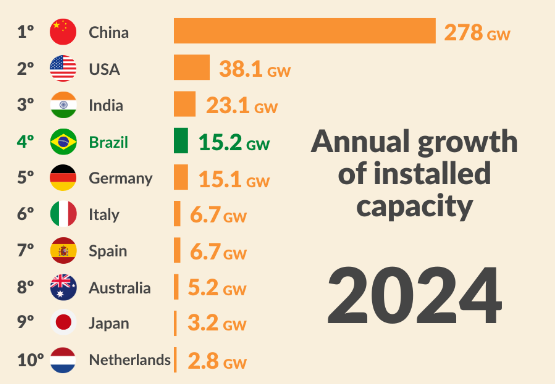
Nos últimos anos, a capacidade de produção de energia eólica e solar no Brasil tem crescido significativamente, sendo o desenvolvimento da energia solar particularmente rápido. A proporção de energia solar no total da produção de eletricidade tem aumentou de 2,2% em 2020 para 13% em 2025, um crescimento de cerca de seis vezes em cinco anos.
Este crescimento tem tido um impacto positivo no sistema elétrico do Brasil. Dado que a energia hidroelétrica tem flutuações sazonais, o rápido desenvolvimento da energia eólica e solar ajuda a aliviar a pressão operacional sobre as centrais hidroeléctricas durante os períodos de seca, promove a afetação racional dos recursos hídricos e, por conseguinte, melhora a estabilidade global da rede eléctrica.
Com o aumento contínuo da procura de eletricidade, o Brasil enfrenta uma situação com oportunidades e desafios. Por um lado, as fontes de energia limpa, como a solar e a eólica, constituem um caminho viável para satisfazer a procura de eletricidade; por outro lado, são também necessárias medidas políticas de apoio e investimentos contínuos para garantir o desenvolvimento saudável das energias renováveis.
Qual é a atual situação regulamentar da Paragem Rápida da Energia Solar no Brasil?
Em 2025, o Brasil lançou ABNT NBR 17193:2025que estabelece especificações de segurança para sistemas fotovoltaicos, incluindo a função de desligamento rápido. É de esperar que a função de desligamento rápido se tenha tornado uma configuração obrigatória para sistemas fotovoltaicos em telhados residenciais, comerciais e industriais no Brasil, o que também reflecte que os regulamentos locais relevantes estão a ser gradualmente melhorados.
Desafios que ainda precisam de ser resolvidos
Embora o Brasil tenha feito progressos significativos na promoção da adoção da DER, ainda enfrenta alguns desafios de implementação:
- Aplicação inconsistente dos regulamentos: Os requisitos de DER variam muito entre as diferentes regiões; algumas aplicam-nos rigorosamente, enquanto outras estão ainda na fase de recomendação.
- Problemas de compatibilidade do sistema: Alguns sistemas fotovoltaicos mais antigos são difíceis de reequipar diretamente com RSD, exigindo potencialmente modificações na cablagem ou substituições de componentes.
- Sensibilização e formação insuficientes: Os instaladores e os proprietários ainda têm uma compreensão limitada das novas normas, e a formação e a educação sobre os produtos precisam de ser reforçadas.
Por que o desligamento rápido é importante para projetos de instalação solar no Brasil?
Mesmo sem um requisito nacional obrigatório, a tecnologia de desligamento rápido ainda oferece uma vantagem fundamental para o contexto único do Brasil:
- Reforçar a segurança
O sistema de corte rápido pode reduzir os riscos eléctricos que os bombeiros enfrentam quando combatem incêndios em edifícios. Esse sistema pode cortar rapidamente o circuito de corrente contínua da energia solar, reduzindo a possibilidade de choque elétrico de alta tensão. Essa função tem valor prático em diversos ambientes urbanos e rurais do Brasil.
- Preparar-se para as necessidades futuras
Dado que os regulamentos relevantes podem ser sucessivamente introduzidos, a instalação de um interrutor de desconexão rápida agora pode ajudar a cumprir os futuros requisitos de conformidade. Esta abordagem de implementação antecipada pode também evitar investimentos adicionais devido a futuras renovações.
- Apoiar a integração na rede
Com os crescentes requisitos operacionais da rede eléctrica brasileira, as tecnologias de segurança, como a desativação rápida, podem dar apoio à gestão da ligação à rede solar e ajudar a conseguir um acesso mais ordenado à rede.
 O futuro do desligamento rápido no Brasil
O futuro do desligamento rápido no Brasil
Com base nas tendências actuais, espera-se que os regulamentos de segurança solar do Brasil sejam gradualmente reforçados. Embora o cronograma específico para um requisito de desligamento rápido obrigatório em todo o país não tenha sido definido, vários sinais indicam que é altamente provável que esse requisito seja implementado:
- À medida que as aplicações solares se generalizam, as normas de segurança correspondentes estão a receber mais atenção.
- Prossegue a coordenação com as normas internacionais.
- Algumas instituições de seguros podem incorporar dispositivos de segurança como a paragem rápida nas condições da apólice.
Conclusão
Embora o Brasil não exija atualmente a instalação de sistemas de desligamento rápido em todo o país, a adoção desta tecnologia pode ajudar a aumentar a segurança do sistema e a sua adaptabilidade a futuros regulamentos. Com o desenvolvimento contínuo da indústria de energia solar no Brasil e a melhoria contínua dos requisitos da rede, as tecnologias de segurança, como o desligamento rápido, tornar-se-ão gradualmente uma parte importante dos sistemas de energia renovável.
Sugere-se que seja considerada uma função de encerramento rápido nos projectos de energia solar. Isto pode não só aumentar a segurança do sistema, mas também ajudar a adaptar-se a possíveis ajustamentos regulamentares futuros.
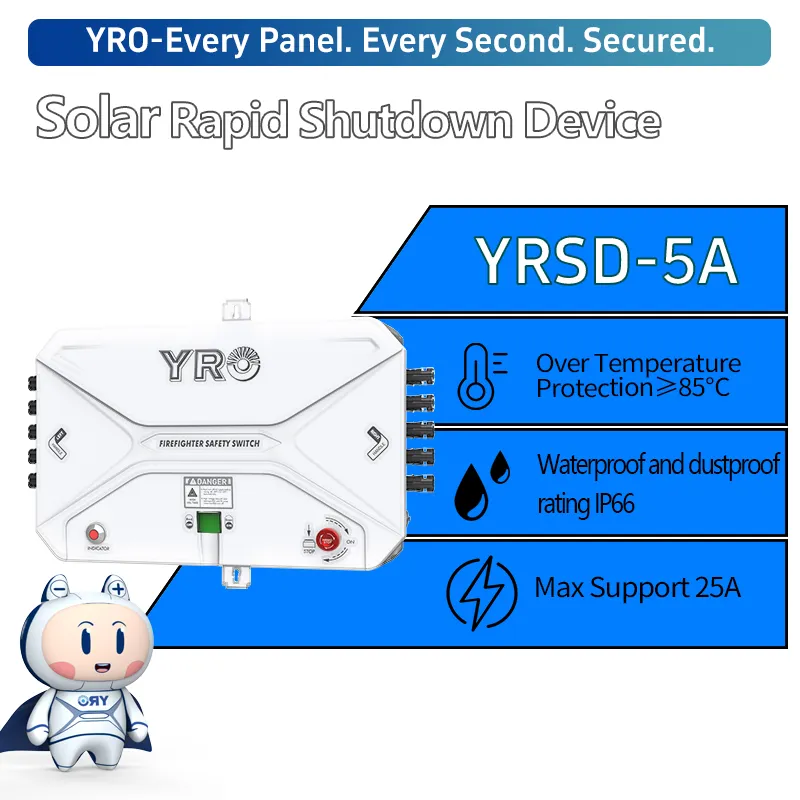
Se você precisa saber sobre uma solução de desligamento rápido adequada para as condições locais no Brasil, não hesite em contactar-nos. A YRO pode fornecer informações de referência sobre a seleção e implementação técnica relevante.

 O futuro do desligamento rápido no Brasil
O futuro do desligamento rápido no Brasil







